- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-14 Origin: Site

Injection molding is a crucial process in manufacturing, creating precise, high-quality parts. But what happens when you need multi-material components in one piece?That's where two-shot injection molding comes in. This technique combines two materials or colors in one cycle, improving both functionality and aesthetics.In this post, you'll learn what two-shot injection molding is, how it works, and why it's so valuable across industries.
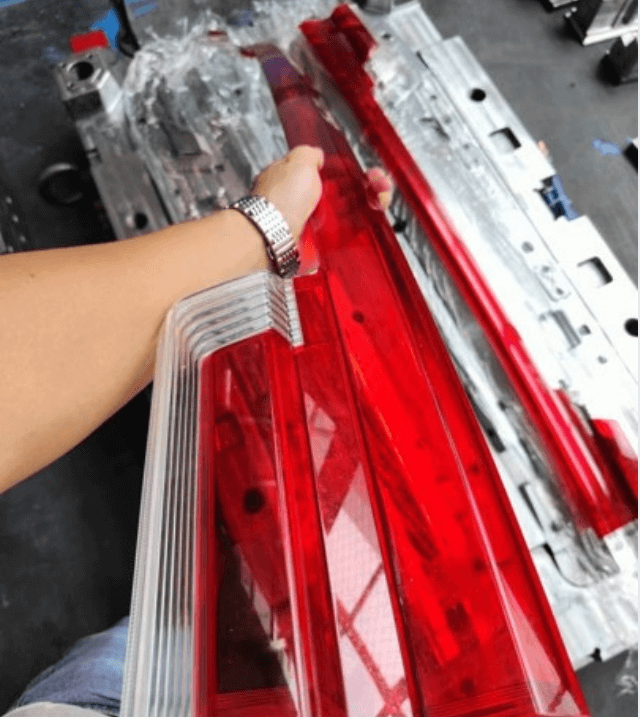
Two-shot injection molding, also known as dual-shot molding, multi-shot molding, or 2K molding, is a manufacturing technique. It combines two different materials or colors into a single part within one molding cycle.
This method reduces the need for post-molding assembly and improves part strength, durability, and aesthetics. It’s widely used when parts need to have multiple textures, colors, or materials, all integrated seamlessly.
The process begins with the first material being injected into the mold to form the base of the part. Once the first material is in place, the mold rotates or shifts to allow the second material to be injected. This second material bonds with the first, creating a finished part.
A specialized injection molding machine is used, equipped with two injection units. These machines allow for precise control of injection speed and pressure, ensuring that both materials blend effectively.
The mold design is critical, with features like mold rotation or indexing ensuring accuracy. Each part of the mold needs to align perfectly for the materials to bond without deforming the part.
Two-shot injection molding offers several advantages. It improves manufacturing efficiency by reducing the need for additional assembly steps. By integrating two materials or colors in a single process, it also cuts down on labor costs.
This method is perfect for high-volume production, as it creates parts with fewer errors and lower costs. It allows for the creation of high-quality, complex parts in one go, making it a reliable choice for large-scale production.
The main advantages of two-shot molding include:
Increased efficiency and reduced assembly costs
Creation of high-quality, integrated parts
Significant savings in high-volume manufacturing
One of the key benefits of two-shot molding is its ability to combine different textures, colors, and materials in one part. This opens up a world of design possibilities, enhancing both the functionality and visual appeal of the product.
For example, in the automotive industry, two-shot molding is used to create dashboards, buttons, and grips with varying textures and colors. In medical devices, it helps create ergonomic tools with soft grips and rigid structures. Similarly, in consumer electronics, this process is used to manufacture sleek, functional parts like phone cases and remote controls.
Some industries that benefit from enhanced aesthetics and functionality include:
Automotive: Parts with varying textures for better usability
Medical: Devices with both soft-touch and rigid components
Consumer Electronics: Sleek, multi-colored parts for gadgets and tools
Two-shot injection molding stands out for its ability to complete the entire process in a single cycle. This helps speed up production times and cuts down on costs, as there’s no need for post-molding assembly. By using just one machine for the whole process, manufacturers reduce the complexity of the operation and minimize human error.
The key benefits of one molding cycle in two-shot molding include:
Faster production with reduced lead times
Lower overall manufacturing costs
Less need for additional assembly labor
Another major advantage of two-shot injection molding is the ability to combine different materials in one part. This can include flexible materials like TPE or rigid ones like ABS, or even varying colors to create visually appealing and functional parts.
Some commonly used materials in two-shot molding are:
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Rigid and durable
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers): Flexible, soft-touch components
Polycarbonate: Strong and heat-resistant
By combining materials, manufacturers can create parts with diverse properties, like a soft grip on a rigid base, all in one process.
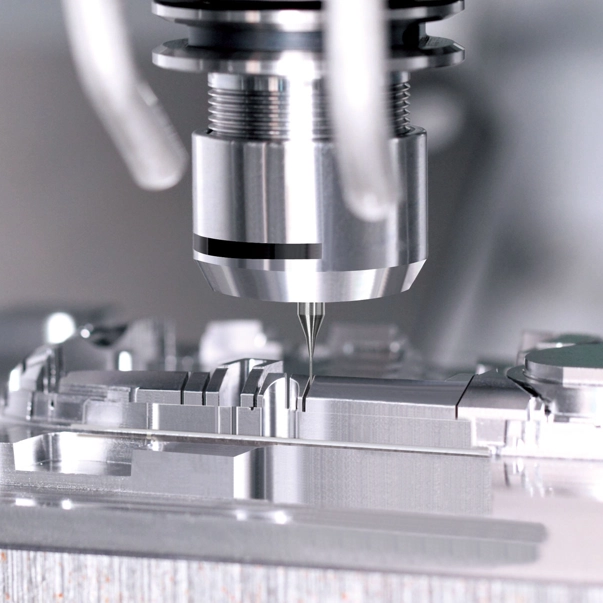

Two-shot molding is widely used in the automotive industry to create parts that require different textures and colors. For example, dashboards, buttons, and grips often have a combination of soft-touch and rigid features for both aesthetic appeal and functionality.
Key automotive applications include:
Dashboards with soft-touch surfaces
Buttons with different textures for better grip
Grips for steering wheels and controls
Two-shot molding in the automotive industry offers high durability and flexibility in design.
In medical device manufacturing, two-shot molding is used to create ergonomic and functional tools. The process allows for combining rigid and soft materials, such as making medical grips with soft-touch features for better user comfort.
Examples of medical devices made using two-shot molding:
Surgical tool handles with soft grips
Non-slip surfaces for medical devices
This technique enhances the functionality and safety of medical tools, providing a higher level of precision and comfort.
The consumer electronics industry benefits from two-shot molding to create complex parts that require both design flexibility and durability. This includes mobile phone cases, wearable devices, and buttons, where multiple materials and colors are needed for both aesthetic and functional purposes.
Some uses in consumer electronics:
Mobile phone cases with flexible edges and rigid backs
Wearable devices with soft-touch buttons
Buttons with varying textures for better tactile feedback
Two-shot molding for consumer electronics enables the production of sleek, functional, and long-lasting products.
Two-shot injection molding is not limited to just automotive, medical, and electronics. It’s also used in everyday products like household appliances, toys, and tools, where both durability and design are key.
Examples of everyday products:
Appliance handles with multiple colors and materials
Toys with soft-touch grips
Household products with complex textures and multi-material designs
In these industries, two-shot injection molding improves both the look and feel of products while maintaining their functional integrity.
Overmolding is another injection molding technique used to combine two different materials, but it differs from two-shot molding in several ways. In overmolding, a rigid substrate is molded first, then placed into a second mold where a softer material is injected over the top. This creates a bond between the two materials, usually through mechanical interlocks.
The key difference between overmolding and two-shot molding is the process flow. Overmolding typically requires two separate molding steps, while two-shot molding completes the process in one cycle.
Process: Two-shot molding uses a single cycle to inject both materials into the same mold, whereas overmolding involves two separate steps, injecting the first material, then overmolding with a second material.
Cost: Two-shot molding is generally more cost-effective for high-volume production due to its efficiency. Overmolding, however, can be more economical for smaller production runs since it uses simpler equipment and setup.
Material Compatibility: In two-shot molding, materials must bond chemically or physically to ensure strength and durability. In overmolding, the materials don’t need to be as compatible since the second material bonds mechanically.
Production Volume: Two-shot molding is ideal for large-scale production runs, offering speed and precision. Overmolding is often more suitable for low to medium-volume production where flexibility in materials is more important.
In summary, while both methods integrate multiple materials into a single product, they are best suited for different production needs, depending on factors like volume, material compatibility, and cost.
Two-shot injection molding offers many benefits, especially for high-volume production. It significantly boosts production efficiency by combining two materials or colors in one cycle, reducing the need for additional assembly steps.
Here are the main pros of two-shot injection molding:
High production efficiency: Two-shot molding reduces cycle time, allowing faster production.
Complex parts with fewer assembly steps: Complex multi-material or multi-color parts are created without post-processing.
Cost-effectiveness for high-volume production: Lower labor and assembly costs make it ideal for large production runs.
Better material bonding and consistency: Materials are injected together, ensuring stronger bonds and more consistent parts.
While two-shot injection molding is highly efficient, there are some challenges to consider. The most notable drawbacks are related to cost and material compatibility.
The key disadvantages of two-shot molding include:
High initial mold and machine costs: Specialized molds and machines are required, which can drive up initial costs.
Material compatibility challenges: Not all materials bond easily, which may limit material choices or require additional modifications to the mold.
Despite these cons, the benefits often outweigh the challenges, particularly for large-scale production.
Two-shot injection molding relies on specialized machinery to achieve precision and efficiency. The machines are equipped with independent injection units, each capable of injecting different materials or colors into the mold at precise speeds and pressures. This allows for seamless integration of multiple materials into a single part without defects.
Key features of two-shot molding technology include:
Independent injection units: Each unit controls a separate material injection, allowing precise timing and pressure control.
Mold alignment: Ensures perfect material bonding and prevents defects.
Precision control: High-tech sensors and controls manage speed, pressure, and alignment, resulting in consistent, high-quality parts.
These features work together to create complex parts in a single cycle, improving production efficiency.
Mold rotation plays a key role in two-shot molding. After the first material is injected, the mold rotates or shifts, positioning the part for the second material. This step requires advanced systems like indexing systems or rotary platens.
Indexing systems: These systems rotate the mold between injection stages, positioning it precisely for the second material injection.
Rotary platens: Used in more advanced setups, these rotating platforms allow for quick and precise mold adjustments.
These technologies ensure the mold aligns correctly, improving precision and reducing the chances of errors, such as misalignment or material contamination.
Material compatibility is a crucial factor in two-shot injection molding. For the process to work smoothly, the materials used must bond properly. If the materials don’t bond well, the final product may not have the desired strength or durability.
Challenges can arise when selecting materials. For instance, some plastics may have different melting points or chemical properties, making bonding difficult. To solve this, engineers often choose materials that have similar properties or use specific techniques, like adding primers or modifying the mold surface.
Key considerations for material compatibility:
Bonding properties: Ensure materials bond chemically or mechanically.
Temperature resistance: Materials should withstand similar temperatures during injection.
Flexibility in material choice: Use materials that work well together, or consider pre-treatment methods.
Two-shot injection molding is most beneficial for high-volume production runs. As the process involves high initial setup costs for molds and machinery, it becomes more cost-effective as production scales.
For large runs, the efficiency of creating multiple parts with different materials or colors in one cycle is ideal. The cost per part decreases as the production volume increases, making it a go-to solution for mass production.
Key points about production volume:
High-volume suitability: Best for large batches where setup costs are amortized.
Cost scaling: Production becomes cheaper per part as volume increases.
Consistency: Ideal for high-volume parts that require consistent quality.
The upfront costs for two-shot injection molding can be high, especially for mold and machine setup. However, these initial costs can be offset by the savings in labor and assembly. Since the entire process happens in one cycle, the need for post-molding assembly is eliminated, reducing overall costs.
Factors influencing cost efficiency include:
Initial mold and setup costs: Expensive, but necessary for large-scale production.
Reduced labor costs: No additional labor is needed for assembly or finishing.
Long-term savings: High-volume production leads to cost reductions in the long run.
When calculating overall costs, it’s important to factor in both short-term setup costs and long-term savings.
When choosing a manufacturer for two-shot injection molding, expertise is key. The process requires advanced machinery and precision to ensure high-quality parts. An experienced manufacturer will have the knowledge to select the right materials, manage complex molds, and deliver consistent results.
Here’s what to look for in a manufacturer:
Reliability: They should consistently deliver high-quality products on time.
Cost-effectiveness: Ensure they offer competitive pricing without compromising quality.
Precision: They should have the expertise to handle complex multi-material parts.
Working with a trusted partner ensures your project runs smoothly and meets industry standards.
Requesting a quote for two-shot injection molding is straightforward, but there are key details you’ll need to provide. A detailed quote helps ensure accurate pricing and a smooth manufacturing process.
Steps to request a quote:
Provide part designs: Share your CAD files or design specs.
Specify materials: Indicate the materials you plan to use for each shot.
Discuss production volume: Provide an estimate of how many parts you need.
Set deadlines: Mention any important timelines or delivery dates.
Factors that affect pricing:
Material selection: Different materials have varying costs.
Mold complexity: More intricate molds can raise costs.
Production volume: Larger orders typically lower the cost per unit.
By providing these details upfront, you can receive an accurate, tailored quote.
Two-shot injection molding offers key benefits like high efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced material integration. It’s ideal for creating complex parts with multiple materials, especially in industries like automotive, medical, and consumer electronics.
If you're working on a project requiring high-volume production and complex components, consider exploring two-shot molding.
Contact us for more information on how two-shot injection molding can benefit your next project.
A: Common materials include ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), polycarbonate, TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers), and TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane). These materials are chosen for their ability to bond well and withstand injection molding pressures.
A: Yes, two-shot molding is cost-effective for high-volume production. While initial setup costs are higher, it reduces labor and assembly costs in large runs, lowering the per-part cost.
A: Unlike traditional molding, two-shot molding uses two materials in a single cycle, creating multi-material parts without additional assembly, making it ideal for complex designs.
A: Industries like automotive, medical, consumer electronics, and appliances benefit from two-shot molding, as it enhances functionality and design flexibility.
A: Yes, two-shot molding allows the creation of complex parts with multiple textures, colors, and materials, offering high design flexibility.