1) Injection Molding
How it works Molten plastic is injected into a metal mold under high pressure, then cooled and ejected.
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-08 Origin: Site

A concise, engineer‑friendly overview of the main plastic molding processes—how they work, where they shine, and how to select the right one for your product.
Plastic molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, shaping everything from consumer packaging to precision medical devices. Understanding the main plastic molding types helps engineers, designers, and procurement teams pick the most efficient and cost‑effective path from concept to scale.
Plastic molding heats and shapes polymer materials inside a mold to produce a solid form. After cooling, the part retains its geometry and properties. The method is valued for high precision, repeatability, and scalability across automotive, packaging, and electronics.
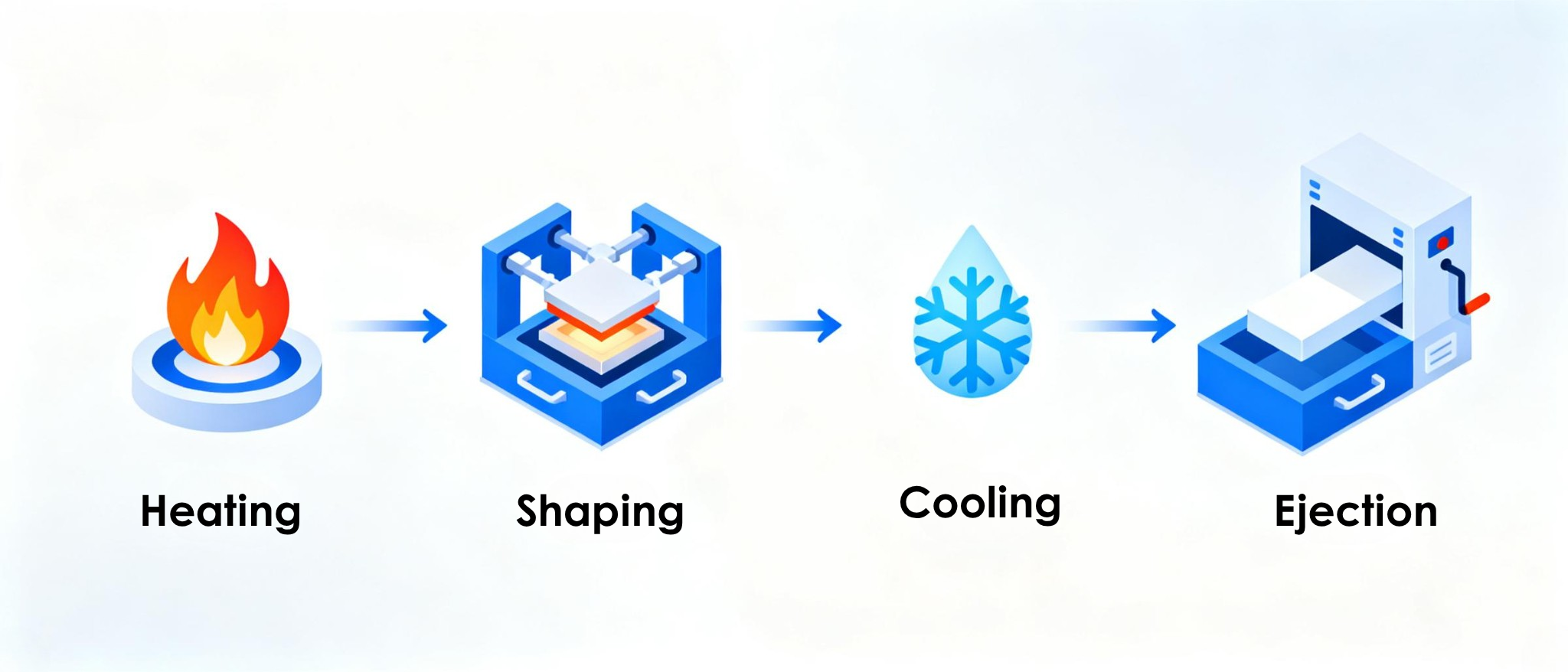
How it works Molten plastic is injected into a metal mold under high pressure, then cooled and ejected.
How it works Heated plastic is inflated inside a mold to form hollow products.
How it works Preheated plastic—often a thermoset—is compressed in a heated mold until cured.
How it works Plastic powder melts and coats the interior of a slowly rotating mold.
How it works Melted pellets are pushed through a die to form continuous profiles.
How it works A heated plastic sheet is vacuum‑formed over a mold.
How it works Filament is melted and deposited layer by layer to build a part.
Balance cost, speed, accuracy, and volume to narrow your options. Use the table below for a quick side‑by‑side view.
| Type | Cost | Speed | Accuracy | Ideal Volume | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection | $$$ | Fast | High | High | Automotive parts, electronics |
| Blow | $$ | Fast | Medium | High | Bottles, tanks |
| Compression | $$ | Medium | Medium | Medium | Electrical components |
| Rotational | $$ | Slow | Low | Low–Medium | Tanks, playground gear |
| Extrusion | $ | Very Fast | Medium | Continuous | Pipes, profiles |
| Thermoforming | $ | Medium | Medium | Medium | Packaging, trays |
| 3D Printing | $$ | Slow | High | Low | Prototypes |
Consider these levers when selecting a molding type:
Production volume: High‑volume runs → Injection or Blow Molding.
Size & geometry: Large, hollow items → Rotational Molding.
Budget & tooling: Limited budget or prototypes → Thermoforming or 3D Printing.
Material performance: Thermosets → Compression; Thermoplastics → Injection.

Injection molding is the most widely used due to its precision, speed, and scalability across many industries.
Thermoforming and extrusion typically carry the lowest tooling costs, making them cost‑effective for simpler parts or continuous profiles.
Yes. With proper maintenance and storage, molds can last for thousands of cycles.
Injection produces solid parts with tight tolerances; blow molding creates hollow items like bottles and tanks.
Get practical guidance on materials, tooling, and unit economics for your next product run.