- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-14 Origin: Site
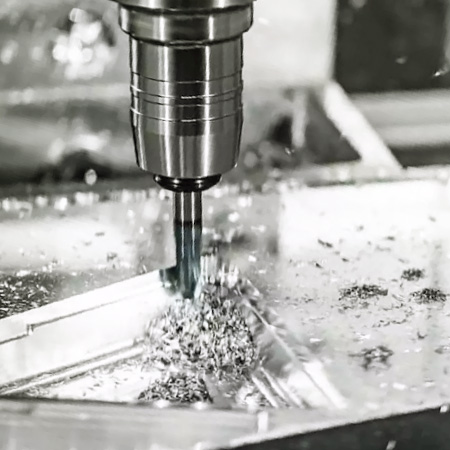

Plastic injection molding is one of the most versatile and efficient ways to manufacture plastic parts at scale. From toothbrush handles to automotive components, it's likely that many plastic items you use daily were made using this process. At the heart of it all lies the injection mold—a custom tool that brings product designs to life. In this guide, we’ll take you step by step through how plastic injection molds are made, from the initial idea to the final mold trial.
A plastic injection mold is a specialized tool used to shape molten plastic into a final product. Made typically from hardened steel or aluminum, the mold comes in two halves: the cavity (female side) and the core (male side). When closed together, they form a hollow space that matches the shape of the desired part. During the molding process, hot plastic is injected into this space under high pressure, and once it cools, the part is ejected—ready for use.
Mold Base: The foundation that supports all other parts of the mold.
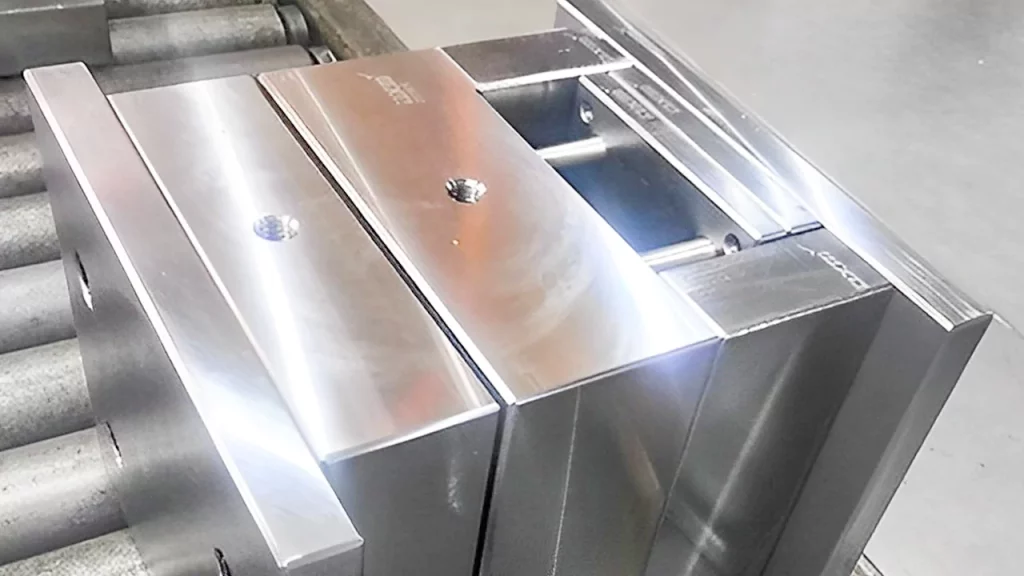

Cavity and Core: These form the outer and inner shapes of the part.
Sprue, Runners, and Gates: Pathways that channel molten plastic into the mold cavity.
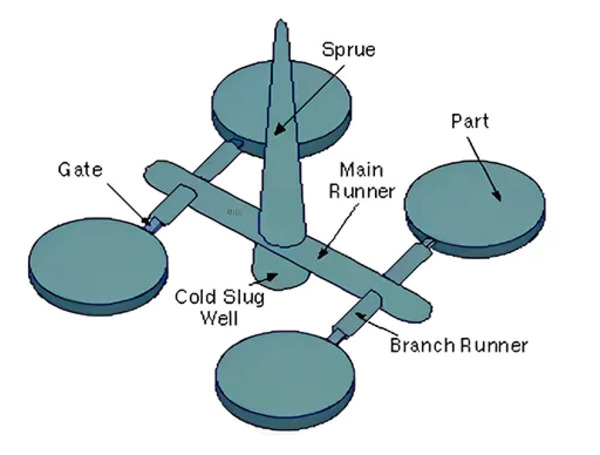
Cooling System: Tubes or channels that circulate coolant to regulate mold temperature and reduce cycle time.

Ejection System: Mechanical pins or plates that push the solidified part out of the mold.
It all begins with a part that’s designed for manufacturability. This means paying attention to features like consistent wall thickness, adding draft angles for easier ejection, and avoiding undercuts where possible. CAD software is your go-to tool for creating a 3D model that's ready for mold design.
With the part model ready, mold engineers get to work designing the mold itself. This involves selecting the parting line, determining gate and runner locations, and designing cooling and ejection systems. Tools like Moldflow or SolidWorks Mold Tools help simulate how the plastic will flow and cool, reducing trial-and-error later on.

P20 Steel: A balanced choice for medium-volume runs.
H13 Steel: Highly durable and suitable for long-run production.
Aluminum: Easier to machine and perfect for prototyping or low-volume projects.
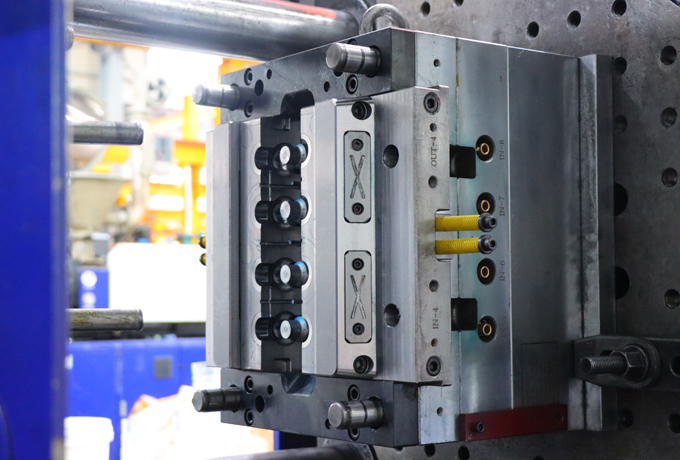
The design now becomes reality through machining techniques such as CNC milling, EDM (electrical discharge machining), and surface grinding. Accuracy at this stage is critical to ensure the two halves of the mold align perfectly and operate smoothly.

Once all parts are machined, the mold is assembled. Mold surfaces are then polished to achieve the desired finish on the molded part—whether matte, glossy, or textured. A good polish also helps with easier ejection and reduces wear.

Initial testing begins with a T1 trial, where plastic is injected into the mold to produce the first set of parts. These samples are closely inspected for issues like short shots, flash, sink marks, or warping. Based on the results, engineers make necessary adjustments before moving toward mass production.
Part Complexity: More complex designs require more intricate molds.
Material Choice: Durable steel alloys cost more than aluminum but last longer.
Tolerances: Tighter tolerances mean longer machining time and higher precision.
Cavitation: Molds with multiple cavities increase upfront cost but reduce unit price.
Prototype Molds: Typically take 2–4 weeks.
Production Molds: For high-volume use, it may take 2–4 months from design to validation.
Think manufacturability early in the product design phase.
Use simulation tools to anticipate flow, cooling, and potential defects.
Collaborate closely with mold makers and get their input during the design stage.
Test early and iterate—prototyping saves time and money in the long run.
Making a plastic injection mold isn’t just about cutting steel—it’s about transforming a concept into a mass-producible reality. While the process involves technical precision and engineering, it also benefits from creativity, planning, and collaboration. With the right approach, your mold can deliver millions of high-quality parts efficiently and reliably.
CAD Tools: SolidWorks, Fusion360, Siemens NX
Mold Design Guides: DME, HASCO standards
Simulation Software: Autodesk Moldflow, Moldex3D